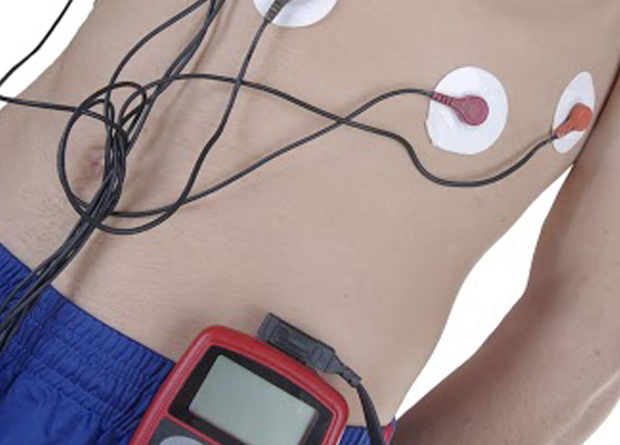
Ambulatory blood pressure (ABP) monitoring involves measuring blood pressure (BP) at regular intervals (usually every 20–30 minutes during the day and every 60 minutes during the night) over a 24 hour period while patients undergo normal daily activities, including sleep.
The portable monitor is worn on a belt connected to a standard cuff on the non-dominant upper arm and uses an oscillometric technique to detect systolic, diastolic and mean BP. When complete, the device is connected to a computer that prepares a report of the 24 hour, day time, night time, and sleep and awake (if recorded) average systolic and diastolic BP.